
Just like MBR, it also manages the creation and organization of partitions on the HDD. Next, the MBR activates the boot sector of the drive to launch the OS. The PC’s/motherboard’s basic input/output system (BIOS) looks for the device with an MBR, and then it executes the volume boot code from the partition that has it. This identifier ensures that the correct drive and partition reads and writes data when using several disks, and it ensures proper PC functionality and security protocol for all read/write data transactions.
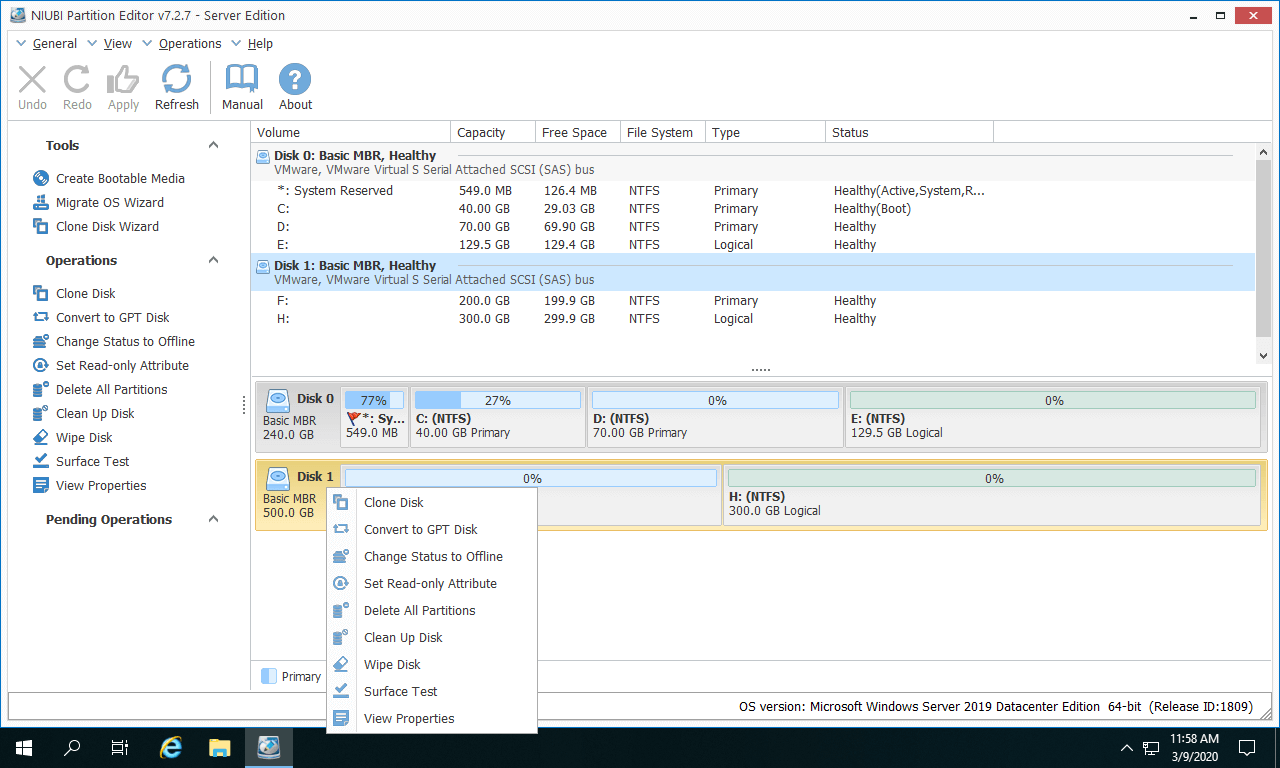

MBR manages how partitions are created and organized on the hard disk drive (HDD). Another reason to use partitions is to install multiple operating systems on the same HDD (Linux, Windows10, Windows 7, etc.) What is MBR?
For instance, many laptops have a “system” partition where everything in the Windows Operating System (OS) goes (often the C: drive), plus a hidden “recovery” partition that can get used to restore the system in case of an accident. Windows displays them as drives in File Explorer, even though they are on the same hard disk drive (HDD). Partitions are separate sections on a hard drive that the operating system uses to boot and function. To understand both MBR and GPT, you should understand what a partition is.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
